KPIs a.k.a Key Performance Indicators are metrics measured typically in organization settings to evaluate business performance. Typically, organizations set up KPIs in the beginning of the year and then evaluate or track the progress towards the targets. The insight gained from KPIs are the most critical insight which helps ensure the organization is performing in the right direction or not. Lack of KPI, or the right KPI or proper tracking may impact the organization adversely and leave the decision makers empty handed at the time of a situation.
Given the criticality of KPI, it is important that the KPIs are set up with care across the organization and then a process is defined and followed. In this blog, we will look at a number of factors to be taken into consideration while setting up KPI for your organization or for an individual.
Select KPI – First step of the process in setting up a KPI is to select the KPI to be measured. This is the most important activity of all as getting this wrong can impact the whole outcome. Selecting the KPI should first of all be based upon the overall objective which is another topic in itself, but once an objective has been selected, the KPI to measure the attainment of the objective should be selected. While selecting this KPI, it is important to ensure that this KPI has direct correlation to the objective set so that the performance of this KPI can help achieve the objective.
Set Target – Once the KPI has been selected, setting target is the next step and fairly easy activity. While selecting KPI targets, it is important to ensure that the target is not too high or not too low. It should be set up to achieve the objective, no more or less. Achieving more or less sometimes has a negative impact which should be taken into consideration if you are setting up stretch targets.
Define Frequency – Frequency is the interval during which you will measure the KPI. Based on this frequency, you will track the KPI performance of the past period. Typically the KPis are tracked in regular intervals such as daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, bi-annually or even annually. The interval selection should depend on the velocity of change in this data. As an example, overall profitability of the business is tracked at monthly or quarterly levels, but the performance of a level 4 process contributing to the overall profitability is tracked weekly or even daily.
Confirm Data source – In no specific order, it is important that the data source for the KPI and the frequency of tracking should be confirmed against the data availability and mechanism of calculation. This has to be clearly defined to avoid any confusion. Confirming data sourcing will cover the source of data, the data preparation steps and finally the calculation method.
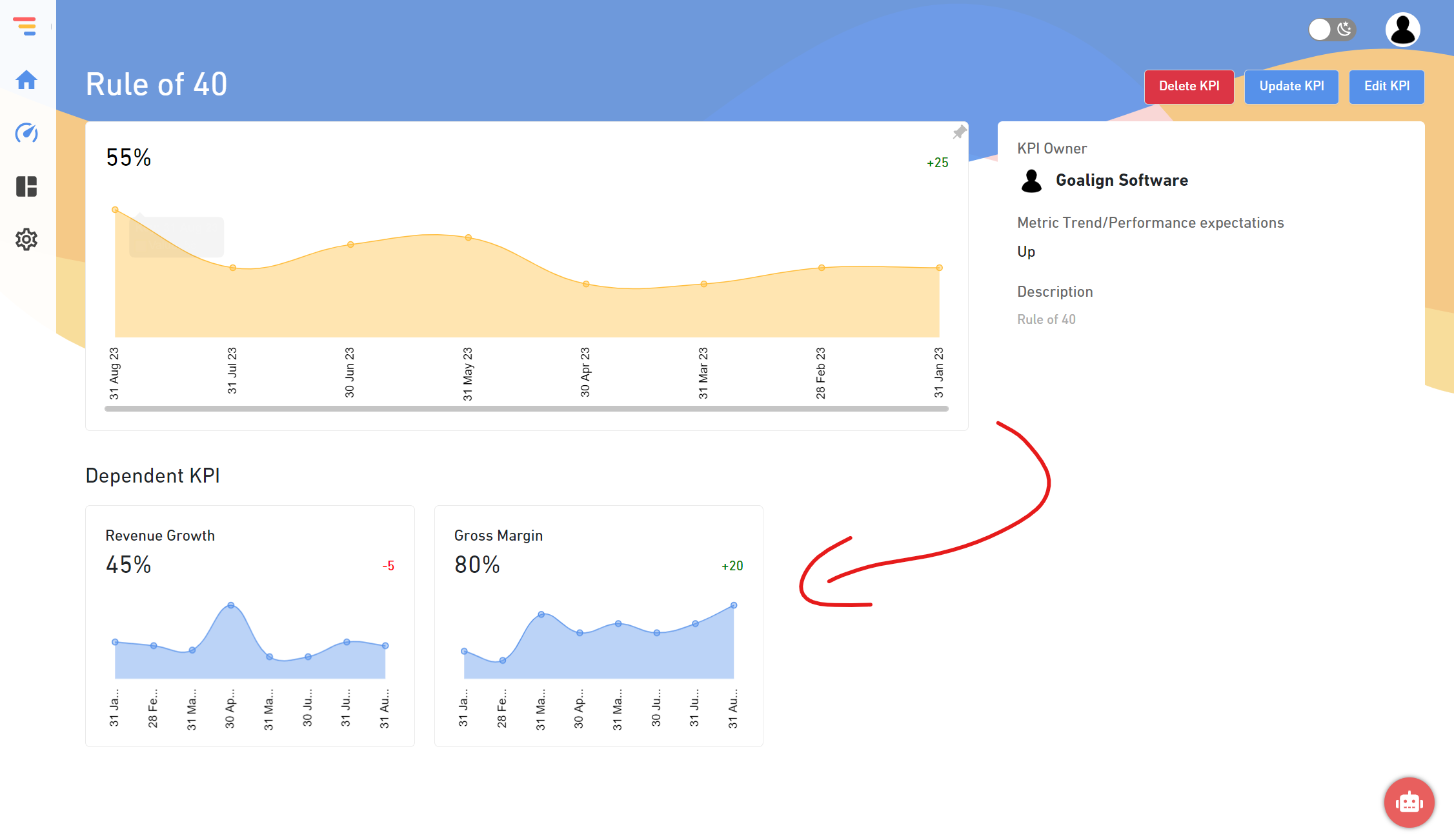
Assign Ownership – Last step in finalizing the KPI is to assign the owner to the KPI. This ensures that the person who is the owner is not only responsible for achieving targets, but tracking and reporting them as per the frequency.
Once the above are taken care, you are all set up to track and report the KPIs. If you are currently doing it in excel or dashboard, we recommend and welcome you to use Goalign. Goalign is a performance management tool which allows organizations to track and report on their OKR and KPI performance and use this data to make predictions and recommend decisions and receive all of this as a power point report into your inbox.